
India is a land of contrasts, with its vibrant culture and rich history. However, beneath the surface lies a complex web of challenges that India faces on a daily basis. From poverty to corruption, from gender inequality to environmental degradation – India’s problems are pressing and multifaceted.
We have provided below well researched and detailed essay on problems with India for your knowledge and information. After going through this essay you will know some of the most significant issues India is facing today and explore their root causes. Let’s examine how these challenges affect everyday life in one of the world’s most populous countries. This essay will be extremely useful in your school/college assignments where you have to write an essay, give speech, or take part in a debate competition.
Essay on Problems with India
India’s problems are complex and pressing
India’s problems are multifaceted and complex, ranging from socio-economic challenges to political unrest and environmental issues. These problems have been persistent for decades, if not centuries, and have deep-rooted causes that require a comprehensive approach to solve.
A closer look at India’s problems
India is a country with diverse cultures and traditions, but it also faces several complex challenges that affect its growth and development. From socio-economic issues to political unrest, India’s problems are multifaceted and need to be addressed systematically. We have categorized these issues for your convenience. Let’s dive deeper-
Socio-economic Issues:
India faces a range of socio-economic issues that affect its people’s quality of life. The most significant among them are poverty, unemployment, economic inequality and lack of basic amenities such as clean water, sanitation and electricity.
Addressing these socio-economic challenges should be at the forefront for policymakers aiming towards building an inclusive economy that benefits all citizens irrespective
Poverty

Poverty is one of the most pressing problems that India faces today. Despite significant economic growth over recent years, poverty remains a persistent issue in many parts of the country.
One of the main reasons for this is inequality. The gap between rich and poor in India is among the widest in the world, with a small percentage of people controlling a large proportion of wealth and resources.
This has led to widespread deprivation among those at the bottom end of society. Many are unable to afford basic necessities like food, clothing, shelter and healthcare.
Another factor contributing to poverty is unemployment. With rapid population growth and limited job opportunities available, many struggle to find work or earn enough money to support themselves and their families.
Addressing poverty will require not just economic growth but also greater social investment in education, healthcare and other essential services. It will also require policies aimed at reducing income inequality and promoting greater inclusion for all members of society.
Unemployment
Unemployment is one of the most pressing problems India is facing. With a population of over 1.4 billion, providing employment opportunities to all has become an arduous task for the government.
The unemployment rate in India reached an all-time high of 7.2% in February 2019, which translates into millions of people without jobs. The situation has only worsened with the COVID-19 pandemic causing massive layoffs across various industries.
One of the major reasons for unemployment in India is the lack of skill development among youth and limited job opportunities in rural areas. The education system also fails to provide practical skills that can translate into employable skills.
Another contributing factor is automation and technological advancements replacing manual labor, leading to further job losses.
Furthermore, there exists a mismatch between industry requirements and academic curricula. Graduates often find themselves underprepared for available job opportunities or forced to take up low-paying jobs due to a lack of relevant skills.
Addressing this issue requires concerted efforts from both public and private sectors by investing in skill development programs, promoting entrepreneurship, encouraging foreign investment and creating favorable business environments.
Economic Inequality

Economic inequality is one of the biggest problems that India is facing today. The divide between the rich and poor continues to widen, with a small percentage of people controlling a majority of the wealth in the country.
This economic disparity can be seen in various sectors, such as education and healthcare, where those with money have access to better quality facilities while others are left struggling. Additionally, it has led to significant social tension and unrest as marginalized communities feel excluded from mainstream society.
One cause for this inequality could be traced back to unequal distribution of resources and opportunities across regions. Rural areas suffer due to lack of investment in infrastructure development which restricts their ability to participate in economic activities leading them into poverty trap.
The government has attempted various measures like reservation policies but without addressing systemic issues causing poverty and income inequalities such efforts may not yield desired results.
It is crucial for policymakers to focus on reducing this gap through targeted interventions aimed at creating greater equality both within and between different socio-economic groups. Only then can we ensure inclusive growth that benefits all sections of society equally
Lack of basic amenities (clean water, sanitation, electricity)
India is a country that struggles with providing its citizens with basic amenities, including access to clean water, sanitation, and electricity. The lack of these facilities has become one of the biggest problems India is facing today.
Clean water is a fundamental necessity for life; however, millions of Indians do not have access to it. According to UNICEF, about 163 million people in India lack access to safe drinking water. This leads to numerous health issues such as diarrhoea and other waterborne diseases.
Sanitation is another significant issue that plagues India. Nearly half of the Indian population still practice open defecation due to a lack of proper toilets or sewage systems. This results in poor hygiene and an increased risk of disease transmission.
Electricity accessibility remains another setback faced by many rural areas in India where power cuts are frequent occurrences leading to darkness at night time which increases crime rates and risks their safety.
The Indian government acknowledges these pressing issues but progress has been slow-moving despite several initiatives launched over the years aimed towards addressing them. It will take collaborative efforts from both public and private sectors along with active participation from the citizens themselves if we hope ever we want things improved upon sooner rather than later for those millions affected by this issue across all corners of our vast nation.
Following are some of the Initiatives by the government to Eradicate Socio-economic Issues-
1.Poverty Alleviation Programs:
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) provides job opportunities and income support to rural households.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana aims to provide access to banking services, insurance, and pension schemes to promote financial inclusion.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system ensures direct transfer of subsidies and welfare benefits to beneficiaries, reducing leakages and corruption.
2. Skill Development and Employment Generation:
- Skill India Mission focuses on providing vocational training and improving employability through various skill development programs.
- Make in India initiative encourages domestic manufacturing and promotes job creation in different sectors.
- Startup India program promotes entrepreneurship and supports the growth of startups through various incentives and funding opportunities.
3.Social Welfare Schemes:
- National Social Assistance Program (NSAP) provides financial assistance to vulnerable sections, including the elderly, widows, and persons with disabilities.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) aims to provide affordable housing to the urban poor.
- National Health Mission (NHM) focuses on improving healthcare infrastructure, reducing maternal and child mortality rates, and providing free healthcare services in rural areas.
4. Education Reforms:
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) aims to achieve universal elementary education by providing free and compulsory education to all children aged 6-14 years.
- Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA) focuses on improving secondary education infrastructure and quality.
- National Scholarship Portal provides scholarships and financial assistance to students from disadvantaged backgrounds.
5. Financial Inclusion:
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana provides loans to micro and small enterprises to promote entrepreneurship and self-employment.
- Jan Aushadhi Scheme offers affordable generic medicines to the masses through dedicated stores.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana provides crop insurance to farmers against losses due to natural calamities.
6.Digital India Initiative:
- Promotes the digitization of government services, digital infrastructure development, and digital literacy programs to bridge the digital divide and enhance access to information and services.
Issues regarding Education in India
Education is a significant problem in India, with a large percentage of the population remaining illiterate. While there have been efforts to improve access to education and increase literacy rates, many challenges remain.
Illiteracy

Illiteracy is one of the biggest problems India is facing. According to a report by UNESCO, India has the highest number of illiterate adults in the world. The literacy rate in rural areas is much lower than that in urban areas.
One of the major reasons for illiteracy in India is poverty. Poor families cannot afford to send their children to school or pay for books and uniforms. Children are also forced into labor at an early age, depriving them of education opportunities.
Another reason for illiteracy is lack of access to quality education. Many schools, especially in rural areas, do not have proper infrastructure or trained teachers. This leads to poor quality education and high dropout rates among students.
Gender inequality also contributes to illiteracy as girls are often deprived of education opportunities due to social norms and traditions. They are expected to stay at home and help with household chores instead of going to school.
The government has launched several initiatives such as Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (Education For All) and Mid-Day Meal Scheme but more needs to be done to eradicate illiteracy from the country.
Illiteracy remains a pressing problem for India affecting millions of people across different regions and demographics which requires urgent attention from both government authorities as well as civil society organizations alike if we hope build towards a better future where everyone can reap equal benefits from society’s resources regardless socioeconomic status or gender identity .
Lack of Access to Quality Education
One of India’s most pressing problems is the lack of access to quality education. While there have been significant improvements in enrollment rates, many children still don’t receive an education that prepares them adequately for their future.
In rural areas, where a significant portion of the population resides, schools are often understaffed and under-resourced. This leads to overcrowded classrooms and teachers who struggle to provide individual attention to each student.
Furthermore, there is a stark difference between educational opportunities offered in urban versus rural areas. Urban students have access to better-equipped schools with more qualified teachers, while those in rural areas are left behind due to limited resources.
Moreover, high dropout rates plague the Indian education system as well. Inadequate infrastructure coupled with financial instability forces many students out of school before they can complete their studies.
The effects of this lack of proper education extend beyond just personal frustration or disadvantage; it has far-reaching consequences on the economy as well. A poorly educated workforce means fewer job opportunities and lower productivity levels overall.
It is crucial for India’s policymakers and civil society leaders alike to ensure that every child receives a quality education regardless of their background or location. It will require collaborative efforts from all stakeholders involved but could prove instrumental in driving progress across various sectors over time.
High dropout rates

One of the major issues plaguing India’s education system is high dropout rates. Many children, particularly those from poor backgrounds, are unable to complete their schooling due to a variety of factors.
One reason for this is the lack of quality education in government schools. Teachers may be absent or unqualified, leaving students without proper guidance and support. Additionally, these schools often lack basic amenities such as clean water and functioning toilets, making it difficult for students to attend regularly.
Another factor contributing to high dropout rates is poverty. Families struggling financially may need their children to work instead of attending school in order to make ends meet. This can lead to children dropping out early in order to contribute income.
The gender gap also plays a role in high dropout rates. Girls are often pulled out of school earlier than boys due to social norms surrounding marriage and household responsibilities.
Addressing these issues will require significant investment and reform within the education system. Providing better facilities and qualified teachers will help retain students who might otherwise leave school early. Additionally, programs that address poverty reduction can help ensure that families do not have to rely on child labor for income generation purposes.
Education Inequality Between Rural and Urban Areas
Education is one of the cornerstones of the development and progress of a country. However, when it comes to India, there are significant disparities in education between rural and urban areas.
The quality of education in rural areas is often inferior due to lack of resources such as qualified teachers, infrastructure facilities like classrooms and libraries.
Moreover, children living in remote villages have limited access to technology which can enhance their learning experience. On the other hand, urban schools offer better teaching facilities with advanced technologies which provide a more comprehensive learning environment for students.
Due to this inequality gap between rural and urban areas’ education systems, many children from underprivileged backgrounds are unable to receive proper schooling. This can lead them towards low-paying jobs or even poverty since they cannot compete with those who have received top-notch educational opportunities.
In addition to these challenges faced by disadvantaged groups living in rural areas, another obstacle that hinders equal opportunity for all is the language barrier. Many schools teach only in regional languages instead of English – making it challenging for students interested in pursuing higher studies or employment prospects outside their state boundaries.
Therefore bridging this disparity requires extensive efforts aimed at providing adequate resources like buildings equipped with modern technologies coupled with trained faculty members so that every child has equal access regardless if they live within an urban or rural area setting.
The government is actively trying to solve the educational issues in India. Some of the most important initiatives of the Government are given below-
Right to Education (RTE) Act:
- The RTE Act makes education a fundamental right for children aged 6 to 14 years.
- It mandates free and compulsory education, ensuring access and enrollment of all children in schools.
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA):
- SSA aims to achieve universal elementary education by providing free and compulsory education to all children aged 6 to 14 years.
- It focuses on improving school infrastructure, teacher recruitment and training, and promoting inclusive education.
Mid-Day Meal Scheme:
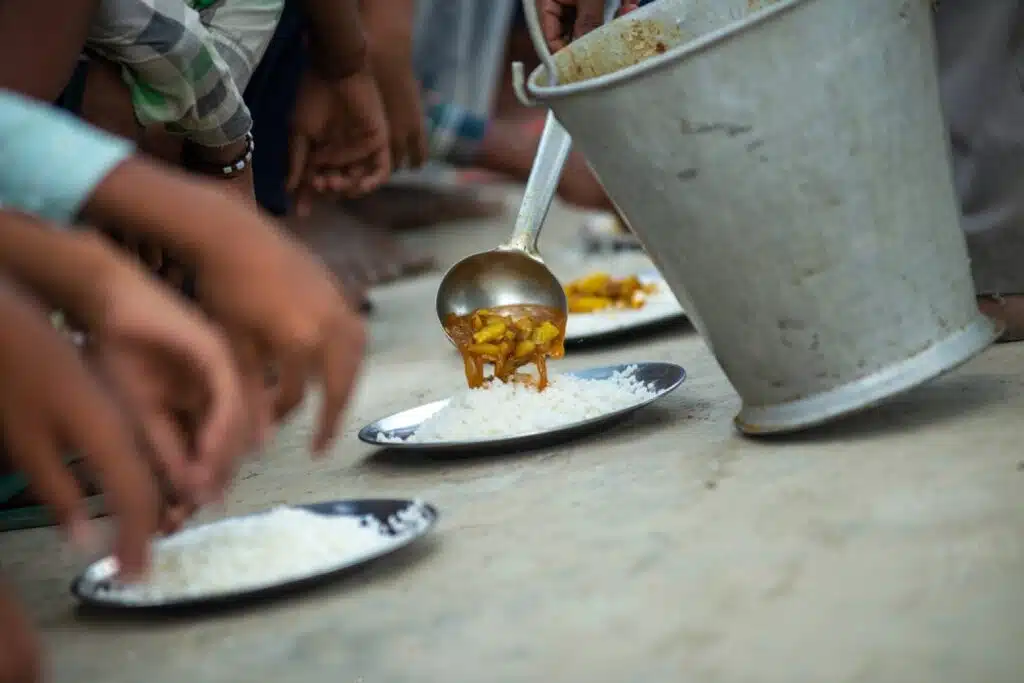

- The Mid-Day Meal Scheme provides free meals to school children to improve their nutritional status and encourage enrollment and regular attendance.
- It aims to enhance the learning outcomes and overall well-being of students.
- Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA):
- RMSA focuses on improving the quality of secondary education and expanding access to secondary schools.
National Scholarship Schemes:
- The government offers various scholarships to economically disadvantaged and meritorious students to promote access to higher education.
- Schemes like the National Means-cum-Merit Scholarship, Central Sector Scholarship Scheme, and others provide financial support for students.
Digital Initiatives:
- Digital initiatives like Digital India and e-learning platforms promote the use of technology in education.
- Initiatives like SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds) provide free online courses and resources for students and teachers.
Vocational Training and Skill Development:
- Skill India Mission focuses on providing vocational training and skill development programs to enhance employability.
- It offers courses in various sectors and promotes entrepreneurship and self-employment.
Teacher Training and Recruitment:
- The government emphasizes teacher training programs to enhance the quality of teaching.
- Initiatives like the National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE) and District Institutes of Education and Training (DIETs) focus on teacher development.
Infrastructure Development:
- The government invests in improving school infrastructure, including classrooms, libraries, laboratories, and sanitation facilities.
- It aims to create a conducive learning environment for students
Health and Sanitation Issues in India:
Health and sanitation are critical issues that India is facing today. Despite the government’s efforts to improve healthcare facilities, a significant portion of the population still lacks access to adequate medical care. Malnutrition remains a serious problem in many parts of India, especially among children.
Malnutrition
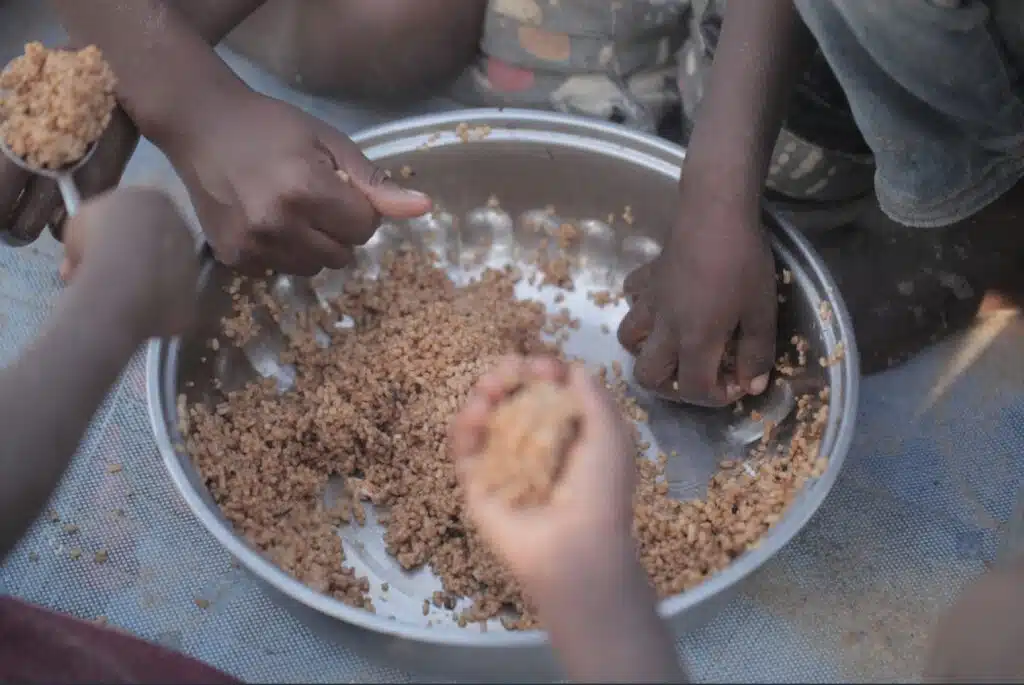

Malnutrition is a serious problem in India, particularly among children. According to UNICEF, 20% of the world’s malnourished children live in India. Malnutrition can lead to stunted growth and development, weakened immune systems, and increased susceptibility to illness.
Several factors contribute to malnutrition in India. Poverty is a major issue as many families cannot afford nutritious food or access healthcare facilities. Additionally, lack of education and awareness about proper nutrition exacerbates the problem.
The government has launched several programs aimed at reducing malnutrition such as the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) scheme which provides supplementary nutrition, health check-ups and pre-school education for young children. However, there are still challenges with implementation and accessibility of these programs.
Addressing malnutrition requires comprehensive solutions including increasing access to nutritious food sources through agriculture policies and improving healthcare infrastructure for early detection and treatment of malnourishment cases.
Tackling malnutrition remains a pressing challenge that requires coordinated efforts from various stakeholders including government agencies, NGOs and individuals alike.
Inadequate Healthcare Facilities
One of the pressing problems that India is facing today is inadequate healthcare facilities. Despite being one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, millions of Indians still lack access to basic healthcare services.
The government spends a mere 1.3% of its GDP on healthcare, which is significantly lower than other developing countries. As a result, there is a severe shortage of doctors and medical staff in rural areas where most people live.
Moreover, most public hospitals are poorly equipped and understaffed. Patients often have to wait for hours or even days to receive treatment due to long queues and limited resources.
This situation has been further aggravated by the COVID-19 pandemic as hospitals were overwhelmed with patients due to insufficient beds and equipment. Many people lost their lives due to this crisis because they could not receive timely medical attention.
It’s high time for India’s government and policymakers to take measures towards improving the country’s healthcare infrastructure. This can be achieved by increasing budgetary allocation towards health-related initiatives, building more hospitals, investing in technology-driven solutions like telemedicine, and incentivizing medical professionals working in rural areas. Only then will India be able to provide adequate healthcare facilities for all its citizens irrespective of their geographical location or economic status.
High Infant Mortality Rate

India’s high infant mortality rate is a pressing problem that needs immediate attention. According to UNICEF, India accounts for the highest number of newborn deaths in the world, with around 600,000 infants dying within the first month of life every year.
The main causes of infant mortality in India are premature births, low birth weight, and lack of access to healthcare facilities. Many mothers give birth at home without proper medical assistance or prenatal care which increases risks for both mother and baby. Additionally, many babies are born with infections due to poor hygiene practices during delivery.
Lack of adequate nutrition also plays a significant role in infant mortality rates as malnourished mothers often give birth to underweight babies who have weak immune systems. Even if these infants survive childbirth, they face an increased risk of death from preventable diseases such as pneumonia or diarrhea.
Despite government efforts to improve maternal and child health through initiatives such as Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY), there is still much work needed to decrease infant mortality rates in India. Greater investments must be made towards improving healthcare infrastructure and increasing accessibility for marginalized communities where maternal and child deaths are higher than average.
Sanitation and hygiene issues
Sanitation and hygiene issues are amongst the most pressing problems that India is facing today. A large proportion of the population still lacks access to proper sanitation facilities, which has resulted in a high incidence of diseases like diarrhea, cholera, typhoid fever, and hepatitis.
Moreover, open defecation remains a common practice in many parts of the country due to insufficient toilets or lack of awareness. The impact on public health is significant as it pollutes water sources and spreads various infections.
In addition to this, waste management is also an area where India faces challenges. Most towns and cities don’t have adequate garbage disposal systems leading to mismanagement of waste materials which often end up littering streets or causing harm to marine life when dumped into oceans.
The government has initiated several programs such as Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (Clean India Campaign) aimed at improving sanitation and hygiene conditions by building more toilets and promoting cleanliness practices. However, there is still a long way to go in addressing these issues effectively.
Solving sanitation and hygiene-related problems requires concerted efforts from all stakeholders including governments at different levels, communities themselves through behavior change campaigns as well as civil society organizations working towards creating awareness about good hygienic practices among people.
The government is actively trying to solve the Health related issues in India. Some of the most important Health related problem solving initiatives of the Government are given below-
National Health Mission (NHM):
- NHM aims to provide accessible, affordable, and quality healthcare services, especially in rural areas.
- It focuses on strengthening healthcare infrastructure, improving maternal and child health, and combating communicable diseases.
Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY):
- PM-JAY is a health insurance scheme that provides financial protection to vulnerable sections of society by offering cashless treatment for serious illnesses and hospitalizations.
- It aims to provide universal health coverage and reduce the financial burden on individuals.
Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (Clean India Campaign):
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan aims to promote cleanliness, hygiene, and sanitation across the country.
- It focuses on building toilets, promoting waste management practices, and ensuring open defecation-free communities.
National Rural Health Mission (NRHM):
- NRHM aims to improve healthcare services in rural areas, with a focus on maternal and child health, immunization, and disease control.
- It emphasizes the training of healthcare professionals and strengthening primary healthcare centers.
National Urban Health Mission (NUHM):
- NUHM focuses on improving healthcare services in urban areas, including slums.
- It aims to provide affordable and accessible healthcare facilities, preventive care, and health education in urban communities.
National Nutrition Mission (Poshan Abhiyan):
- Poshan Abhiyan aims to address malnutrition and stunting among children and women.
- It focuses on providing nutritious meals, promoting breastfeeding, and creating awareness about healthy eating practices.
Clean Drinking Water Initiatives:
- The government has launched schemes like Jal Jeevan Mission to provide piped water supply to all households, ensuring access to clean drinking water.
- It also promotes water conservation and proper water management practices.
National AIDS Control Program (NACP):
- NACP focuses on prevention, control, and management of HIV/AIDS.
- It includes awareness campaigns, testing, treatment, and support services for affected individuals.
Immunization Programs:
- The government runs various immunization programs, including the Universal Immunization Program (UIP), to provide vaccines against preventable diseases.
- It aims to reduce infant and child mortality rates and control the spread of infectious diseases.
Gender Inequality:
Gender inequality is one of the most pressing problems that India faces today. Discrimination against women is still prevalent in many parts of the country, leading to violence and abuse. Women also face limited access to education and healthcare, perpetuating a cycle of poverty.
Discrimination against women
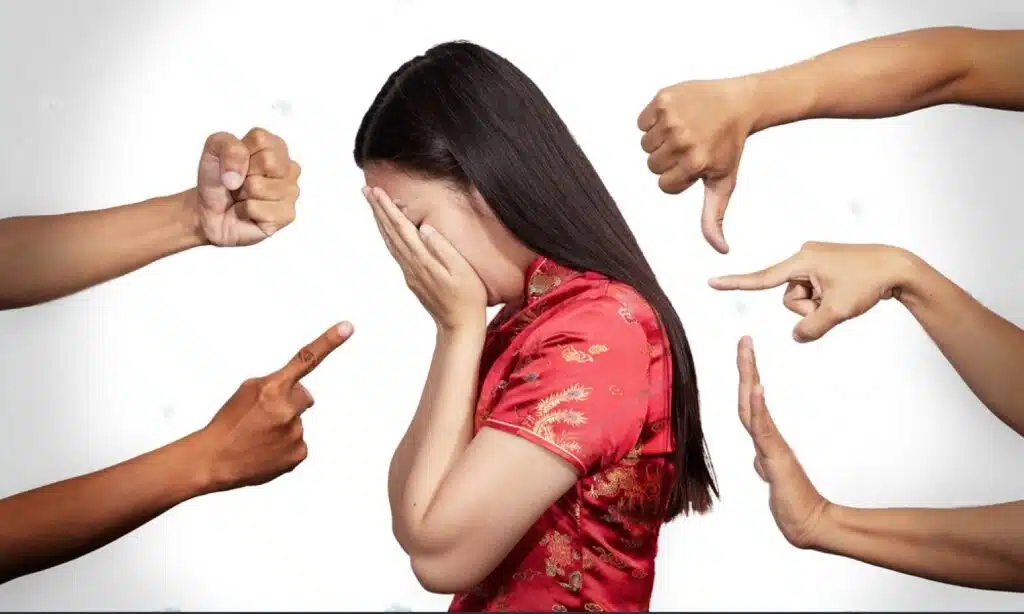

Gender inequality is one of the most pressing problems India is facing. Discrimination against women has been a persistent issue in Indian society, despite efforts to promote gender equality. Women are often treated as second-class citizens and face discrimination in various aspects of life.
One of the biggest challenges women face in India is limited access to education and healthcare. Many families prioritize educating their sons over their daughters, leading to higher illiteracy rates among girls. This lack of education limits opportunities for women and perpetuates the cycle of inequality.
Violence against women is also a major problem in India, with incidents such as rape, domestic violence and honor killings making headlines regularly. Despite government initiatives aimed at protecting women from violence, many crimes go unreported or unresolved due to societal attitudes towards victims.
Furthermore, there exists a gender pay gap where men earn significantly more than their female counterparts for doing the same job. This disparity reflects deep-seated biases against working women that need addressing by both employers and lawmakers alike.
Discrimination against women remains an enormous challenge in India that requires sustained focus and action from all sectors of society if meaningful progress on this front is ever going be made.
Violence against women
Violence against women is a pervasive and serious problem in India that affects women of all ages, classes, and backgrounds. Despite some progress made to address this issue over the years, it remains one of the most pressing problems facing Indian society today.
One of the major forms of violence against women in India includes physical abuse, such as domestic violence. Women are often subjected to beatings by their husbands or other family members who believe they have the right to control and dominate them.
Another form of violence against women is sexual assault and harassment. Women are often targeted for rape or molestation simply because they are female. This type of violence can occur anywhere- on public transportation, at school or work, or even in their own homes.
Additionally, there are instances where dowry-related deaths take place due to non-compliance with demands from men’s families after marriage. Honor killings also remain prevalent in certain parts of India where male relatives kill females who they feel bring shame upon their family.
These acts not only cause significant harm physically but also create an atmosphere where women live with daily fear and anxiety about being attacked or mistreated without any consequences for those committing these crimes against them.
Despite efforts by the government and NGOs to combat this issue through education programs aimed at changing societal attitudes towards gender roles; unfortunately enough hasn’t been done yet which needs immediate attention before it gets too late!
Gender Pay Gap

Gender pay gap is a persistent and pervasive problem in India. Despite numerous efforts by the government and civil society, women continue to earn less than men for doing the same work. This discrimination is not only unfair but also undermines the economic potential of half of India’s population.
One of the main reasons behind this disparity is traditional gender roles that deem men as primary breadwinners while women are supposed to prioritize domestic duties over career advancement. As a result, women often face barriers such as limited access to education, training opportunities, and mentorship which hinders their ability to negotiate better salaries.
Moreover, there exists a lack of transparency in salary negotiations with employers often failing to disclose pay scales or offering vague explanations for differences in wages. Even when companies claim to have policies against gender discrimination, they are not always implemented effectively leading to continued disparities.
It’s high time that we address this issue head-on and ensure that equal pay for equal work becomes a reality rather than just an idealistic notion. We need stricter laws that mandate equal pay for all genders across industries along with measures like job evaluations and audits aimed at identifying wage gaps within organizations.
Additionally, we must challenge societal norms around gender roles through awareness campaigns aimed at promoting greater equality between men and women both inside and outside workplaces. Only then can we hope to create a truly fairer working environment where everyone has an equal opportunity irrespective of their gender identity or expression.
Limited access to education and healthcare for women
India’s gender inequality is not a new concept. Women in India face numerous challenges, including limited access to education and healthcare. In many rural areas of the country, girls are still expected to drop out of school early due to cultural norms and financial constraints.
This lack of education perpetuates the cycle of poverty for women, making it difficult for them to secure well-paying jobs or gain independence. Additionally, with inadequate healthcare facilities available in these areas, women often suffer from preventable illnesses that go untreated.
Furthermore, even when women have access to healthcare services, they may face discrimination and mistreatment at the hands of male medical professionals. This can discourage women from seeking medical help altogether.
The government has implemented various policies aimed at improving educational and healthcare opportunities for women in India. However, more needs to be done to ensure equal access for all women regardless of their socio-economic status or geographic location.
Investing in education and healthcare programs specifically designed for young girls and adult women could provide much-needed support towards breaking down barriers that limit their potential success.
The Indian government has taken several steps to address gender inequality in the country. Here are some of the key initiatives:
Legal Reforms:
- The Prohibition of Child Marriage Act sets the legal age for marriage as 18 for girls and 21 for boys, aiming to prevent early marriages and protect the rights of girls.
- The Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act provides legal protection and support to women facing domestic violence.
- The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act mandates the establishment of internal complaint committees in workplaces to address and prevent workplace harassment.
Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao (Save the Girl Child, Educate the Girl Child):
- This national campaign aims to promote the value and importance of girl children, prevent gender-based sex-selective practices, and encourage their education.
- It includes awareness programs, cash incentives for girl child education, and improved access to healthcare facilities.
Reservation and Representation:
- Reservation policies provide quotas for women in local government bodies (Panchayats and Municipalities) to ensure their political participation and representation.
- The Women’s Reservation Bill, which seeks to reserve one-third of seats in the Parliament and State Legislatures for women, has been proposed but is yet to be enacted.
Economic Empowerment:
- Self Help Groups (SHGs) and Microfinance initiatives provide financial support, training, and entrepreneurship opportunities to women.
- Schemes like Stand-Up India promote entrepreneurship among women and provide loans and support for starting and running businesses.
Gender-sensitive Legislation and Policies:
- The Maternity Benefit Act provides paid maternity leave and other benefits for women in the formal sector.
- The Maternal and Child Health Care Program focuses on improving maternal and child health outcomes and reducing maternal mortality rates.
- The National Policy for Women addresses various issues related to women’s empowerment, safety, and gender-based violence.
Education and Skill Development:
- Initiatives like the Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao campaign and the National Scheme of Incentive to Girls for Secondary Education provide incentives and scholarships to promote girls’ education.
- Skill development programs, such as those under the Skill India Mission, aim to enhance women’s employability and economic independence.
Various campaigns, workshops, and awareness programs are conducted to sensitize society about gender equality, women’s rights, and the importance of gender mainstreaming.
Environmental Challenges:
India’s environmental challenges are vast and complex, affecting the health and well-being of its citizens. With a rapidly growing population and increasing urbanization, these issues have become even more pressing in recent years.
Pollution (air, water, noise)

Pollution is one of the biggest problems India is facing today. The country’s rapid industrialization and urbanization have led to higher levels of air, water, and noise pollution.
Air pollution is a major problem in Indian cities due to the high number of vehicles on the roads. This has resulted in an increase in respiratory diseases such as asthma and lung cancer.
Water pollution is also a serious issue in India due to untreated sewage being dumped into rivers and lakes. This not only affects marine life but also leads to water-borne diseases such as cholera and typhoid.
Noise pollution has become increasingly prevalent with the rise of construction sites, traffic on busy roads, loudspeakers at religious events, and festivals. Noise pollution can lead to hearing damage, sleep disturbance, increased stress levels among other health issues.
The effects of pollution are felt disproportionately by those who live in poverty or near these polluted areas. It’s time for government authorities to take action against polluting industries while promoting cleaner energy sources such as solar power. Education campaigns also need to be conducted so that people understand how their actions contribute towards making this problem worse.
Deforestation
Deforestation is a major environmental challenge that India faces, with significant impacts on the country’s biodiversity and climate. The rapid rate of deforestation has led to soil erosion, loss of wildlife habitat, and reduced water availability.
The primary cause of deforestation in India is human activity such as logging for commercial purposes and clearing land for agriculture. As urbanization increases, forests are being destroyed to make way for infrastructure development projects like roads, dams, and buildings.
This rampant destruction of natural resources has caused significant harm to the environment by accelerating climate change. Forests play an essential role in carbon absorption; however, their removal releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Deforested areas also experience high temperatures due to increased exposure to sunlight leading to desertification.
Moreover, this process exacerbates soil erosion which affects agricultural productivity leading ultimately towards food shortage. This issue demands an urgent response from both individuals and government agencies alike through sustainable forest management practices that preserve ecosystems while accommodating economic growth needs.
Deforestation remains one of India’s most pressing challenges today with dire implications for its ecological balance resulting from unchecked exploitation driven by greed rather than sustainability goals.
Water scarcity

Water scarcity is a significant issue in India, with around 600 million people facing severe water shortages. The situation is further exacerbated by climate change and the country’s rapidly growing population.
The primary cause of water scarcity is poor management and inefficient use of resources. Since agriculture accounts for around 80% of all freshwater consumption, there needs to be a more sustainable approach to irrigation practices. Traditional methods like flood irrigation are highly wasteful and lead to soil degradation over time.
Another factor contributing to water scarcity in India is the lack of investment in modern infrastructure. Many rural areas still rely on hand pumps or wells for drinking water, which can often be contaminated with pollutants such as pesticides or fecal matter.
Moreover, groundwater levels have declined significantly due to excessive pumping, leading to depletion and contamination. As a result, many regions face acute shortages during droughts or periods of low rainfall.
Solving the problem requires both short-term measures like rainwater harvesting systems and long-term solutions such as investing in modern infrastructure like dams, pipelines and treatment plants while also promoting efficient usage practices among farmers.
Addressing water scarcity requires urgent action from policymakers at every level- local authorities must improve their management strategies while central government should increase funding towards better infrastructure development projects that will help combat this pressing issue faced by millions across India today.
Climate change impact
Climate change is one of the most significant problems that India is facing today. The changing climate patterns have devastating effects on agriculture, which employs around half of the population. Droughts and floods are becoming more frequent, causing huge losses to farmers.
The impact of climate change is not limited to agriculture; it also affects other sectors such as energy production and infrastructure development. With rising temperatures, demand for electricity increases leading to overuse and strain on resources.
Moreover, India’s coastal regions are highly vulnerable to sea-level rise caused by global warming. This puts millions of people living in these areas at risk due to flooding and displacement.
Another significant impact of climate change in India is on public health. Heatwaves during summers lead to dehydration, heatstroke, and even death among vulnerable populations like children and elderly citizens. Increased air pollution worsens respiratory illnesses like asthma.
However, despite the challenges posed by climate change in India, there has been a positive shift towards sustainable practices such as renewable energy sources like solar power plants being set up across the country.
It’s important now more than ever for individuals and governments alike to prioritize environmental issues if we want a better future for generations to come.
The Indian government has implemented several measures to address environmental challenges in the country. Here are some of the key steps taken:
National Action Plan on Climate Change:
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) focuses on climate change mitigation and adaptation through the promotion of renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable agriculture, and water conservation.
- National Clean Air Program (NCAP) aims to tackle air pollution in 122 cities by setting time-bound targets, improving air quality monitoring, and implementing pollution control measures.
Renewable Energy Promotion:
- The government has set ambitious targets for renewable energy generation, including solar power and wind energy.
- Initiatives like the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) and the International Solar Alliance (ISA) promote solar power generation and adoption.
Forest Conservation and Afforestation:
- The government has launched initiatives like the Green India Mission and the National Afforestation Program to increase forest cover, promote afforestation, and restore degraded lands.
- The Compensatory Afforestation Fund Act (CAMPA) aims to enhance afforestation activities using funds collected for diversion of forest land.
Waste Management:
- The Swachh Bharat Mission (Clean India Mission) focuses on solid waste management, promoting cleanliness, and eliminating open defecation.
- The Plastic Waste Management Rules regulate the use, collection, and disposal of plastic waste to reduce its environmental impact.
Water Conservation and River Cleaning:
- The Namami Gange (Clean Ganga) mission aims to rejuvenate the Ganga river by preventing pollution, conserving water, and promoting sustainable river management practices.
- The Jal Jeevan Mission focuses on providing tap water connections to every rural household, promoting water conservation, and improving water quality.
Environmental Regulations and Enforcement:
- The Environment (Protection) Act and other environmental laws provide a legal framework for regulating pollution, protecting ecosystems, and enforcing environmental standards.
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) is a specialized court that addresses environmental disputes and ensures compliance with environmental regulations.
International Collaborations and Agreements:
- The government participates in international agreements and collaborations, such as the Paris Agreement on climate change, to address global environmental challenges and work towards sustainable development.
- Public Awareness and Education:
- Awareness campaigns and educational programs are conducted to promote environmental consciousness, sustainable practices, and the importance of conservation.
Corruption:
Corruption is one of the biggest problems India is facing today. It is a widespread issue that affects every aspect of Indian society, from politics to everyday life. Corruption occurs when officials misuse their power for personal gain, rather than serving the public interest.
Widespread corruption in government and institutions
India’s struggle with corruption is a well-known fact. The country has been ranked 86th out of 180 countries on the Corruption Perception Index, indicating widespread corruption in government and institutions. Corruption affects all levels of society, from the highest political offices to everyday interactions between citizens and officials.
The primary concern is that corruption leads to an unequal distribution of resources, where those who are part of the corrupt system benefit at the expense of everyone else. It also creates a vicious cycle where people are forced to engage in bribery and other illegal activities simply to get their work done.
While there have been efforts made by successive governments to curb corruption, it remains a major challenge for India. One important step towards combating this issue would be greater transparency and accountability within government institutions.
It is also crucial for citizens to play an active role in fighting against corruption by reporting any instances they encounter. In addition, public awareness campaigns can help educate people about their rights and how they can protect themselves from becoming victims of corrupt practices.
Tackling corruption will require a concerted effort from both government authorities as well as ordinary citizens. Only then will India be able to make meaningful progress towards achieving its development goals in an equitable manner.
Lack of transparency and accountability
Transparency and accountability are crucial for the smooth functioning of any government or institution. Unfortunately, India has been facing a severe lack of both these virtues in recent years. Corruption and bribery have become rampant, with many public officials involved in black market activities as well.
One of the major reasons for this is the absence of transparency in decision-making processes. Often, key decisions are made behind closed doors without proper consultation or debate, leading to suspicions about motives and outcomes.
Moreover, there is a lack of accountability among those who hold positions of power. Many politicians and bureaucrats believe that they can get away with their wrongdoings without facing any consequences. This makes it difficult to bring about positive change in society.
Another issue contributing to this problem is the complex bureaucratic structure prevalent in India. The sheer number of layers makes it easy for officials to hide information from others and avoid scrutiny altogether.
The media plays an essential role in exposing corruption and holding public officials accountable; however, there have been instances where journalists have faced intimidation or even violence while investigating such cases.
To address this problem effectively, there needs to be greater transparency at all levels – from the way decisions are made to how resources are allocated – coupled with stronger mechanisms for accountability when things go wrong. Only then can India truly move towards becoming a more just and equitable society for all its citizens.
Bribery and black market activities

Bribery and black market activities are significant problems that India faces. Corruption has seeped into every aspect of society, with individuals paying bribes to get things done quickly or to receive special treatment. Unfortunately, bribery is prevalent in government institutions as well, where officials take advantage of their positions for personal gain.
The black market is another area that authorities struggle to control. The sale of illegal goods such as drugs, weapons and counterfeit products have become an everyday occurrence in many parts of the country. These activities not only fuel organized crime but also put people’s lives at risk.
Moreover, these issues cause a ripple effect throughout the economy by increasing prices on essential items like food and clothing. This increased cost ultimately affects those who can’t afford it most – the poor.
To address this problem, there needs to be greater transparency and accountability within government institutions. Laws should be enforced more strictly against those involved in bribery or other corrupt practices.
Furthermore, education campaigns aimed at raising awareness about the consequences of corruption could go a long way towards reducing this issue’s prevalence across all levels of society.
Though we need to acknowledge that these problems won’t disappear overnight; they require sustained efforts from both citizens and governments alike if we hope ever truly overcome them completely.
The Indian government has implemented several measures to address the issue of corruption in the country. Here are some of the key steps taken:
Legislative Framework:
- The Prevention of Corruption Act (PCA) provides a legal framework to prevent corruption, punish offenders, and protect whistleblowers.
- The Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act establish independent anti-corruption ombudsman offices at the central and state levels to investigate corruption complaints against public officials.
Transparency and Accountability:
- The Right to Information (RTI) Act enables citizens to access information held by public authorities, promoting transparency and accountability.
- Online portals and e-governance initiatives have been introduced to enhance transparency in government processes and reduce opportunities for corruption.
Anti-Corruption Bodies:
- The Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) is an apex anti-corruption body responsible for preventing corruption in the central government and public sector organizations.
- State-level anti-corruption bodies, such as Lokayuktas and Vigilance Departments, have been established to address corruption at the state level.
Digitalization and E-Governance:
- Digital initiatives like e-governance, online services, and cashless transactions reduce the need for intermediaries and minimize corruption risks.
- Platforms like the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) promote transparent and corruption-free procurement processes.
Whistleblower Protection:
- Whistleblower protection laws and mechanisms have been enacted to encourage individuals to report corruption without fear of reprisals.
- The Whistleblower Protection Act provides safeguards for whistleblowers and establishes a mechanism for receiving and investigating complaints.
Financial and Economic Reforms:
- Initiatives like demonetization and the implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) aim to reduce black money circulation and improve financial transparency.
- Steps such as the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) help tackle corruption and enhance corporate governance in the business sector.
International Cooperation:
- The government cooperates with international organizations and participates in anti-corruption initiatives like the United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) to combat cross-border corruption and promote global cooperation.
Ethical Standards and Training:
- The Central Civil Services (Conduct) Rules and similar codes of conduct promote ethical behavior among public officials.
- Training programs and capacity-building initiatives are conducted to enhance ethical awareness and integrity in the public sector.
Social Issues:
India’s social issues are deeply ingrained and complicated, stemming from factors such as tradition, religion, and caste. Let’s see deeply and in detail-
Caste discrimination

Caste discrimination is a social problem that has affected India for centuries. The caste system divides people into different categories based on their birth, which leads to discrimination and marginalization of certain groups. Despite being illegal, the practice of casteism still exists in many parts of India.
The caste system is deeply ingrained in Indian society and has led to discrimination against lower castes, who are denied access to education and job opportunities. They also face social exclusion and are often subjected to violence.
Dalits or “untouchables” are at the bottom of the caste hierarchy and continue to suffer from discrimination despite affirmative action policies implemented by the government. They face difficulties accessing basic amenities such as clean water, sanitation, healthcare facilities, and education.
Caste-based violence is another issue that plagues Indian society. Honor killings, forced marriages, physical abuse – all these forms of violence have been reported against those who dare challenge the established norms related to marriage or other societal customs.
Caste discrimination remains one of India’s biggest problems even today and needs immediate attention from both individuals as well as policy-makers alike. It requires a collective effort by everyone in society irrespective of their religion or status towards eradication so that every individual gets equal opportunity without any prejudice whatsoever!
Communal tensions
Communal tensions in India are a result of religious and cultural differences between various groups. These tensions have been prevalent for decades and have led to violence, discrimination, and even riots.
One major cause of communal tension is the lack of respect for different religions and beliefs. People often judge others based on their religion or caste, rather than accepting them as fellow human beings. This leads to feelings of animosity and distrust towards each other.
Another cause is the political manipulation of these differences by certain parties who use them to gain power. They spread hate speech against one community or another, which further fuels existing tensions.
These communal tensions not only disrupt peace but also hinder progress in areas such as education, healthcare, economy etc., affecting all communities equally. It’s high time that we recognize the importance of mutual respect and peaceful coexistence among all communities if we want India to prosper as a whole.
Efforts must be made at every level – from individuals to government – to promote interfaith harmony through education programs and initiatives that celebrate diversity instead of exploiting it. Only then can we hope for lasting peace in our country without any communal strife or discordance anymore!
Honor killings
Honor killings are a heinous crime that have plagued India for centuries. This practice involves killing someone, often female, who is believed to have brought shame or dishonor to the family or community. Such killings are usually carried out by close family members, including parents and siblings.
One of the main reasons behind honor killings is deeply ingrained patriarchal beliefs that place women at a lower status than men. Women who refuse arranged marriages, marry outside their caste or religion, or engage in premarital sex may be seen as defying traditional gender roles and bringing shame onto their families.
Another factor contributing to honor killings is the belief that one’s reputation within the community is more important than an individual’s life. In some cases, village councils known as khap panchayats even issue orders for honor killings as a means of upholding social norms and morality.
Despite laws against honor killings being introduced in India several years ago, these crimes continue unabated due to lack of enforcement and cultural resistance towards change. Families often go unpunished due to fear of retaliation from their communities.
It is crucial for society to recognize that every human life has inherent worth and dignity regardless of gender or societal status. Education on gender equality must be prioritized in order to combat this abhorrent practice once and for all.
Child marriage

Child marriage is a major issue prevalent in India that has detrimental consequences on the lives of young girls. Despite being illegal, it still exists in many parts of the country due to deeply rooted cultural practices and poverty. The practice deprives girls of their childhood and denies them opportunities for education and personal growth.
In rural areas, where child marriage is more common, parents consider their daughters as financial burdens who need to be married off at an early age. This leads to a perpetuation of gender inequality, as boys are given priority over girls when it comes to education and other resources.
The health risks associated with childbirth at a young age are also high, putting both the mother and child’s life in danger. Additionally, these marriages often lead to physical violence and emotional abuse against young brides who lack adequate support systems.
The government has taken steps towards eradicating this practice by increasing awareness through campaigns and implementing stricter laws with harsher punishments for offenders. NGOs have also been working tirelessly towards ending child marriages by providing education programs for children most at risk.
It is crucial that society recognizes the importance of allowing girls to grow up without societal pressures weighing them down before they can make decisions about their futures themselves.
The Indian government has implemented several steps to address social issues in the country. Here are some of the key initiatives:
Social Welfare Programs:
- Various social welfare programs provide financial assistance, healthcare, and other benefits to vulnerable sections of society, such as the Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), Other Backward Classes (OBCs), and economically weaker sections.
- Schemes like the National Social Assistance Program (NSAP), Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY), and Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) aim to provide support and upliftment to marginalized communities.
Reservation Policies:
- Reservation policies ensure representation and opportunities for marginalized communities in education, employment, and political spheres.
- Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and Other Backward Classes (OBCs) have reserved quotas in educational institutions, government jobs, and legislative bodies.
Empowerment and Skill Development:
- Skill development programs like Skill India Mission focus on providing vocational training and enhancing the employability of youth from disadvantaged backgrounds.
- Entrepreneurship promotion initiatives and financial assistance schemes encourage self-employment and economic empowerment.
Women Empowerment :
- Initiatives like Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao (Save the Girl Child, Educate the Girl Child) and the Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana provide support for girl child education and financial assistance for pregnant women.
- Laws and campaigns against gender-based violence, such as the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao campaign and the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, aim to create a safer and more inclusive society for women.
Social Awareness and Sensitization:
- Awareness campaigns, public campaigns, and community mobilization efforts are conducted to promote social awareness and sensitize society about various social issues, such as gender equality, education, health, sanitation, and more.
Social Justice and Human Rights:
Institutions like the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) and State Human Rights Commissions work to protect and promote human rights, ensuring social justice and addressing human rights violations.
Rehabilitation and Social Integration:
Programs and schemes are implemented for the rehabilitation and social integration of marginalized groups, such as persons with disabilities, street children, and victims of trafficking and bonded labor.
Legal Reforms:
- Legislative measures address social issues, such as the Protection of Civil Rights Act, the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, and the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, among others.
These are some of the government steps taken to address social issues in India. The government continues to prioritize social development and implement policies and programs to uplift marginalized communities, promote social justice, and create a more inclusive and equitable society.
Population Growth is Another challenge to India’s Development:
Population growth is one of the most significant challenges that India has been facing for decades. The country’s population is growing at an alarming rate, and it has put a tremendous strain on resources and services.
Overpopulation and its associated challenges

Overpopulation is one of the biggest challenges India is facing today. The country’s current population stands at over 1.4 billion, and it is expected to surpass China as the world’s most populous nation by 2027.
The rapid increase in population has put immense pressure on resources and services such as water, sanitation, healthcare, and education. It has led to a rise in poverty levels and unemployment rates.
Additionally, overpopulation has resulted in uncontrolled urbanization with an influx of people into cities. This has led to a strain on infrastructure facilities such as housing, transportation systems, electricity supply and internet connectivity.
Moreover, overpopulation also poses significant environmental challenges such as pollution (air, water noise), climate change impact due to increased carbon emissions from industrial activities and deforestation for land development purposes.
To address this issue effectively requires concerted efforts from both the government and citizens alike. On the part of the government; implementing effective family planning programs through awareness campaigns about contraception methods can help control birthrates while providing incentives for smaller families can reduce strain on resources.
On their part citizens should adopt responsible family planning measures by seeking appropriate medical advice before deciding how many children they’ll have so that they plan accordingly without putting undue burden on themselves or society at large.
Overpopulation remains among India’s most pressing problems requiring immediate attention from all stakeholders involved in tackling its associated challenges head-on if we want our future generations to enjoy life sustainably within this great land!
Strain on resources and services
India’s rapidly growing population has put a significant strain on the country’s resources and services. With more than 1.3 billion people, India is expected to surpass China as the most populous nation by 2027. This puts immense pressure on India’s natural resources such as water, land, and forests.
The demand for food production has led to deforestation and damage to soil fertility due to overuse of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. The increasing need for energy also poses a challenge as India relies heavily on coal-based power plants which contribute significantly towards air pollution.
The healthcare system is overwhelmed with patients in many areas of the country leading to long waiting times, inadequate medical equipment, shortage of staff and overcrowded hospitals. Additionally, access to safe drinking water remains an issue in many parts of the country which leads to health concerns related to poor sanitation practices.
Infrastructure development is not keeping pace with population growth resulting in traffic congestion during peak hours causing delays in transportation systems that are already insufficiently developed.
Moreover, housing facilities are limited resulting in high property prices making it difficult for low-income earners who often live under precarious conditions or become homeless altogether. All these challenges exacerbate poverty levels across regions where basic needs aren’t met while straining public services provision further at both national-level governance & local municipal administration levels alike.
Uncontrolled Urbanization
Uncontrolled urbanization is one of the most significant problems India is currently facing. Rapid population growth, along with rural-to-urban migration, has led to a surge in demand for housing and infrastructure, which has resulted in haphazard and unplanned development.
This unchecked expansion has brought about numerous challenges, including overburdened transportation systems, insufficient housing facilities, limited access to electricity and internet connectivity, as well as environmental degradation. The lack of proper planning and zoning regulations further exacerbates these issues.
Moreover, uncontrolled urbanization also creates social problems such as increased crime rates due to poor living conditions and inadequate policing. Additionally, it leads to income inequality between those who can afford better quality of life versus those who cannot.
To address this problem effectively requires comprehensive land-use policies that encourage sustainable development practices while balancing economic needs with environmental concerns. It’s crucial for authorities to promote smart city initiatives that prioritize walkability and public transportation options like bikes or electric vehicles instead of cars alone. It would help reduce congestion on roads leading to fewer emissions from traffic flow into the atmosphere.
Finally yet importantly local communities should be involved in decision making processes when addressing matters related directly affecting their lives such as new developments or construction projects nearby residential areas or neighborhoods where they live daily basis allowing greater transparency around what occurs within their surroundings.
The Indian government has implemented several steps to address this issue of overpopulation. Here are some of the key initiatives:
Family Planning Programs:
- The government has been promoting family planning and reproductive health services to encourage responsible parenthood and voluntary control over family size.
- Programs like the National Family Planning Program and Mission Parivar Vikas aim to provide accessible and affordable contraceptives and reproductive healthcare services.
Maternal and Child Health:
- Improving maternal and child health is crucial to reducing population growth. The government has launched various programs, such as the Janani Suraksha Yojana and Integrated Child Development Services, to enhance access to quality healthcare for mothers and children.
Healthcare Infrastructure:
- Strengthening healthcare infrastructure, especially in rural areas, is essential to provide accessible and quality healthcare services, including reproductive healthcare and family planning services.
- The government has been investing in improving healthcare facilities, training healthcare professionals, and expanding the reach of healthcare services to underserved areas.
Socio-Economic Development:
- Promoting socio-economic development, poverty alleviation, and creating employment opportunities can contribute to reducing population growth rates.
- Initiatives like skill development programs, entrepreneurship promotion, and poverty alleviation schemes aim to uplift communities and provide alternative livelihood options.
Political Challenges affecting the Growth of India:
Political challenges are also a pressing issue in India, with political unrest and conflicts being reported from various parts of the country. This is not a new issue. The lack of effective governance has resulted in a breakdown of law and order in many areas.
Political unrest and conflicts

India’s political landscape is marred with unrest and conflicts. The country has witnessed numerous political clashes that stem from various factors such as religion, caste, region or ideology. These issues have led to violence, protests, and even deaths.
One significant factor contributing to the political turmoil in India is the lack of effective governance. Corruption within the system has allowed politicians to manipulate power for their own benefit rather than serving their people. This inevitably leads to public outrage and mistrust towards government officials.
Another reason for the unrest is electoral malpractices where candidates often engage in unfair means of winning an election. This creates an environment of distrust among citizens who question whether their votes truly count.
Regional disparities and tensions further exacerbate the problem by creating a divide between different groups within society. Political parties exploit these differences for their own gain, which can lead to violent confrontations between communities
Furthermore, social media platforms have also played a role in fanning political flames by spreading misinformation and hate speech online. In recent years there are many cases where posts on social media resulted in violence offline during elections or other events.
Until India addresses its underlying governance issues along with addressing regional divisions exacerbated by some politicians only interested in power; it will continue struggling with frequent outbreaks of tension & conflict related problems across its complex socio-political landscape over time
Lack of effective governance
The lack of effective governance in India is one of the most pressing problems facing the country today. Despite being the world’s largest democracy, corruption and inefficiency have long plagued government institutions at all levels.
One of the primary challenges facing India’s governance system is a lack of transparency and accountability. The public has little trust in elected officials, who are often seen as corrupt and self-serving. This has led to widespread apathy amongst citizens towards political processes.
Furthermore, political interference by those in power often undermines independent institutions such as the judiciary or law enforcement agencies. This leads to weakened rule of law, with powerful individuals able to escape punishment for illegal activities.
Another issue is that many policies are poorly implemented or inadequately enforced due to bureaucratic red tape and lack of resources. As a result, schemes aimed at improving social welfare or economic growth fail to achieve their desired outcomes.
Addressing these issues will require significant reforms both within government structures themselves as well as broader societal changes that promote greater civic engagement and accountability from elected representatives.
Electoral malpractices
India’s electoral system is one of the most complex and challenging in the world. Despite its democratic values, many Indian politicians resort to electoral malpractices to win elections.
Electoral malpractices are illegal activities that occur before, during, or after an election aimed at influencing its outcome. These include vote-buying, booth capturing, rigging ballot boxes, impersonation of voters, and intimidation of voters.
During India’s general elections in 2019 alone, there were over 1,200 cases filed for violations related to campaign expenditure by candidates and their parties.
One major challenge in curbing electoral malpractices is the lack of proper enforcement mechanisms. The Election Commission has limited power to enforce laws against these practices effectively.
Moreover, political parties often have a vested interest in engaging in such tactics as they seek power at all costs – even if it means subverting democracy altogether
In recent years various measures have been taken to curb this menace like strict implementation on model code of conduct regulations along with deployment of central armed forces but still a lot needs to be done for fair democracies.
Regional disparities and tensions
India is a diverse country with different languages, cultures, and traditions. However, this diversity also brings regional disparities and tensions that have been challenging to address. One of the major issues in India is the unequal distribution of resources across states.
The southern and western regions are more developed than the northern and eastern parts of India. This disparity has resulted in an economic divide that leaves some areas struggling with poverty while others thrive. Additionally, there are cultural differences between regions which can lead to social tensions and conflicts.
One factor contributing to these regional disparities is the lack of infrastructure development in certain areas. Poor transportation systems make it difficult for people living in remote locations to access education or healthcare facilities easily. Similarly, insufficient housing facilities limit opportunities for economic growth.
Another issue is political representation as some regions feel underrepresented in government decision making processes leading to mistrust among people from those areas towards central leadership.
Addressing regional disparities will require investment into infrastructure development projects such as better transportation systems or improved housing facilities while also ensuring equal participation by all peoples regardless of their region’s location within India’s borders when it comes down civic duties like voting during elections or being appointed positions within government institutions at higher levels where decisions affecting many lives take place heavily influencing policies shaping society over time too!
Conclusion
India is a country with immense potential, but it is plagued by numerous problems that hinder its growth and progress. These challenges are complex, interrelated, and pressing, requiring concerted efforts from the government, civil society organizations, and individuals.
From poverty to corruption, illiteracy to environmental degradation, gender inequality to political instability – India’s problems are multifaceted and require multi-pronged solutions. It’s high time that we address these issues in a holistic manner so that people can live a life of dignity and prosperity.
It will take collective action on all fronts – social reform movements seeking justice for marginalized communities; innovative entrepreneurs creating jobs for millions of unemployed youth; policymakers implementing inclusive policies that benefit all citizens irrespective of their caste or religion; scientists developing sustainable technologies to mitigate climate change impacts – only then will India be able to overcome its pressing problems.
As responsible citizens of this great nation, we must acknowledge our shortcomings while also celebrating our strengths. We need to hold ourselves accountable for making positive changes in our communities as well as supporting those who fight against injustice in any form. By working together towards common goals like education access or clean drinking water supply across rural areas- we can make India better than ever before!